A fascinating thing about user experience (UX) is that we can look in any direction and find applications of user experience in the most mundane or the most advanced projects one can come across. UX is known to save lives, improve things, and improve design. In healthcare, especially, UX is pivotal in ensuring that the patients have the optimum resources available along with the best shot at recovery.
UX In Healthcare: Current Scenario
According to a report by McKinsey & Company, by 2050, one in four people in Europe and North America will be over the age of 65, indicating that the healthcare systems will have to handle an increasing number of patients with complex needs. Managing such patients is predictably expensive and calls for a systemic shift from an episodic care-based philosophy to one that is much more proactive and focused on long-term care management.
Healthcare spending, on the other hand, is simply not keeping up. Without major structural and transformational change, healthcare systems are poised to buckle under pressure. Health systems also need a larger workforce.
But although the global economy could create 40 million new health-sector jobs by 2030, there is still a projected shortfall of 9.9 million physicians, nurses, and midwives globally over the same period, according to the World Health Organization.
There is a pressing need to not just train and retain more healthcare professionals, but also to ensure their time is used where it adds the most value—caring for patients.
*Enters AI in surgery*
Artificial intelligence in surgery is at the forefront of this innovation being carried out in the healthcare industry. With the ratio of healthcare professionals and patients on an unfavorable incline, AI surgery robots, and AI in surgery are not only stepping in to fill the void but also offering accuracy and precision that completely takes out the scope for human error.
In the USA alone, that means saving over 250,000 lives per year.
UX at the forefront of digital surgery
As important as the robots are in surgery, AI is quickly adapting to the human needs of surgery.
AI surgery robots teamed with an effective AI in surgery allow the surgeon to identify the issues with minimal invasion and provide a high-definition view to ensure quicker, and more accurate surgical practices.
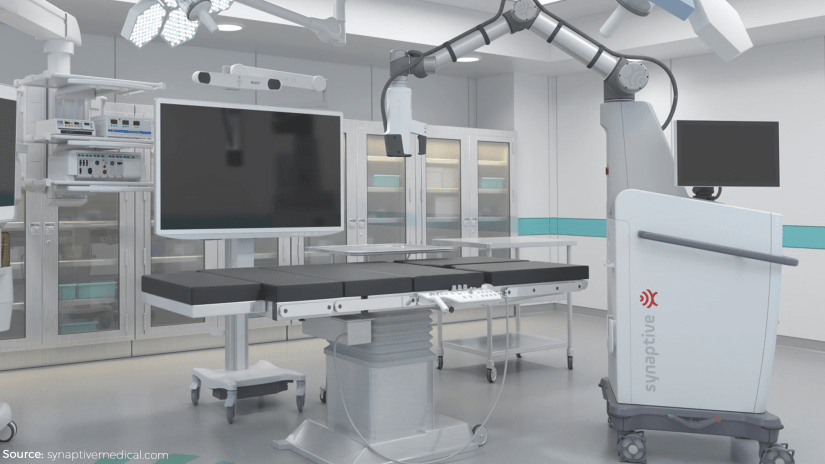
Synaptive conducted user testing for a surgical robot called Modus V. Modus V is a fully automated bot that is being tested to be used by neurosurgeons. The Modus V is equipped with a state of the art software and an AI that is a machine learning pro.
The team had to get down to UX 101 for the testing of Modus V and understand the problems faced by the surgeons to offer viable solutions. The positioning of the camera, automating the surgery through a mechanical arm, and providing the AI surgeons with much-needed accuracy; all of this was the result of applying basic UX principles to complex surgery.
The testing of Modus V was simply a robot-assisted surgery. But it showed the positive effects on what matters the most – the outcome of the surgery. The results for the patients were found to be much more positive with the use of assistive technology than without.
Surgical robot and design
Surgical robots are not only designed to assist with complex surgeries but are also being tested to conduct robotic surgeries through AI and machine learning. The Children’s National Medical Center in Washington recently tested a supervised robot running automated soft tissue surgery. The results were phenomenal and the results of the surgery were shown to be better than a human surgeon.
The project lead on the Smart-Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR) states that the benefit of completely automated robots is well worth the investment. He notes that the availability of the right AI surgeons during emergencies will not hamper the quality of surgery if automated robots become the norm for surgeries. Given that medical mistakes are known to be the third-highest cause of death in the USA, automation seems to reduce the burden on human surgeons to be perfect all the time.
These surgical robots are now being designed with specific surgeries and techniques in mind, testing the AI surgeons for the requirements as well as the issues faced during the actual process of surgery.
The design of the AI in surgery is as important as the design of the robot itself. The program that allows the robot to be unsupervised or partially supervised needs to be exceptionally well-designed due to the stakes at hand. In the case of the automated surgery in STAR, the robot makes the decision of where sutures should go, based on vision and pressure.
This is arguably more accurate than any human surgeon could manage and is only possible due to the strong program that enables the robot. Despite the gigantic strides made to promulgate current technology to the point of clinical use, glaring gaps do remain. For instance, the lack of haptic feedback to the surgeon and the inability of the surgeon to be stationed at the operating table.
The future of robotic surgery holds a significant improvement in the visualization technologies used in the operating room, along with improvements in the robots’ abilities to communicate haptic feedback to the surgeon. This will make way for unparalleled sensation for the surgeon and almost eliminate inadvertent tissue contact and injury.
Improved versions of the user interface will let the surgeon have access to the patient’s bedside, remain sterile throughout the procedure, employ a head-mounted three-dimensional visualization system, and allow the most intuitive master manipulation of the slave robot to date.
Benefits of well designed AI in healthcare for surgical robots
The interest in robotic surgery is rising and the reason is not simply novelty or success rates. Various benefits have been recorded through the recent testing and research that has been undertaken.
Often enough, robots are mistaken as the ones who perform the actual process of surgery. But this stands true as a misconception, at least for now. Thanks to AI-powered advancements in robotics, they can be of great help in assisting surgeons in microsurgical procedures. So, while a robot surgeon can be a far-fetched concept, these AI-powered robots can provide valuable, real-time inputs to enable surgeons to perform better.
A study conducted on 379 orthopedic patients revealed that AI-assisted surgery resulted in 5 times lesser complications compared to the surgeons operating alone.
Automated robots are not humans, they learn through patterns and duplicate results immaculately. This completely takes away the risk of human error associated with surgery. This possibility in itself makes this technology worth exploring and expanding. Additionally, semi-assisted systems like the Da Vinci surgical system, which have been in use for around a decade in the surgical space, have proven to be one of the safest, minimally invasive ways to conduct surgery.
Surgery powered by robots is actively and effectively gaining prominence across a variety of medical procedures including gynecology, orthopedics, thoracic, general surgery, dental implants, neurology, and as well as hair transplants. Robotic technology allows doctors with minimal experience or medical practitioners new to a particular operating procedure to deliver treatment at a level that they would not be able to do even after gaining years of experience. It has also been proved that robot-assisted surgeries help reduce the effects of hand tremors and also constrain accidental movements.
Surgical robots also tackle another major problem that the healthcare industry faces i.e. manpower planning. The doctor-patient ratio is steadily declining and robots are a great way to tackle that. Even with assisted systems, surgeons spend relatively less time in surgery than they do while conducting the surgery manually. If the surgery is automated completely, manpower planning will be a non-issue very soon.
Artificial Intelligence and the Future of surgical robotics
The benefits of surgical robots are abundant and evident, however, there are feasibility issues that can be worked upon with good UX practices. Even so, the evolution of UX in healthcare has resulted in the simplification of complex surgery and lower mortality rates already.
The design of the AI in surgery is as important as the design of the robot itself. The program that allows the robot to be unsupervised or partially supervised needs to be very well designed due to the stakes at hand.










